Pus Cells In Urine : Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
When your routine urine test reveals pus cells, it can be a concerning moment. These cells, also known as white blood cells (WBCs), are typically an indication that something might be wrong within your urinary tract. In this blog, we’ll dive into what pus cells in urine mean, why they appear and how you can address the issue effectively.
What Are Pus Cells In Urine?
Pus cells are essentially white blood cells that are part of your body’s immune system. They play a crucial role in defending against infections and managing inflammation. When these cells show up in your urine, it suggests that there may be an infection or inflammation somewhere in your urinary tract, which includes your kidneys, bladder, ureters and urethra.
Common Causes of Pus Cells In Urine
Several conditions can lead to the presence of pus cells in your urine. Understanding these causes can help in addressing the underlying problem effectively.
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A UTI is the most common reason for pus cells in urine. Infections in the bladder, kidneys or urethra prompt an immune response, which results in an increased number of white blood cells being excreted through urine.
- Kidney Stones : Kidney stones can cause irritation and inflammation of the urinary tract. This irritation can lead to the presence of pus cells as your body tries to fight off the resulting infection or inflammation.
- Interstitial Cystitis : This chronic condition involves inflammation of the bladder’s lining. It can cause symptoms similar to a UTI, including the presence of pus cells in urine.
- Prostatitis : In men, prostatitis or inflammation of the prostate gland, can lead to pus cells in the urine. This condition may be caused by bacterial infections or other factors.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) : Certain STIs can also result in pus cells appearing in urine. These infections can affect the urinary tract, leading to inflammation and an increase in white blood cells.
Pus Cells In Urine Associated Symptoms
The presence of pus cells in urine is often accompanied by symptoms that can help pinpoint the underlying issue. Common symptoms include:
– Frequent and Painful Urination: You may experience discomfort or a burning sensation when urinating.
– Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine: Pus cells can make urine appear murky or have an unpleasant odor.
– Lower Abdominal Pain: Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen may be present, especially if associated with a UTI or kidney stones.
– Fever and Chills: In more severe cases, you might experience systemic symptoms like fever or chills.
Diagnosing the Cause
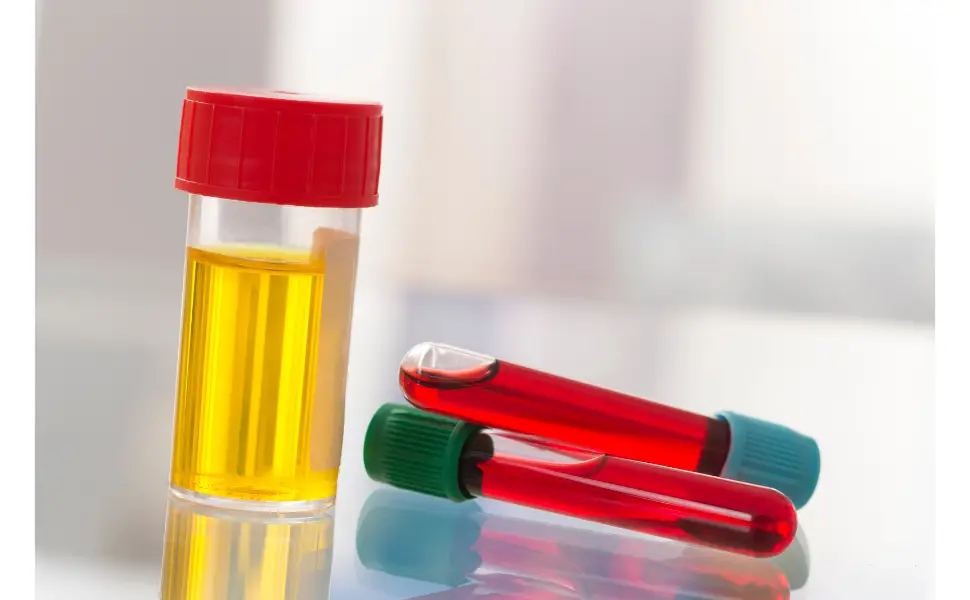

If pus cells are detected in your urine, your healthcare provider will likely conduct further tests to determine the underlying cause. These may include:
– Urine Culture: This test aids in determining the particular bacteria that is causing the illness.
– Ultrasound or CT Scan: Imaging tests can reveal kidney stones or other abnormalities.
– Blood Tests: Blood tests can provide additional information about your overall health and help detect systemic issues.
Treatment Options
The treatment for pus cells in urine depends on the underlying condition:
- Antibiotics : For bacterial infections like UTIs, antibiotics are often prescribed to eliminate the infection and reduce pus cells.
- Pain Management : For conditions causing discomfort, such as kidney stones, pain relievers can help manage symptoms while the underlying issue is addressed.
- Increased Fluid Intake : Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria and may assist in preventing UTIs and kidney stones.
- Specific Medications or Procedure : Conditions like interstitial cystitis or prostatitis may require specialized treatments, such as specific medications or procedures.
Preventive Measures

To reduce the risk of developing conditions that lead to pus cells in urine, consider the following preventive measures:
– Practice Good Hygiene: Proper hygiene can help prevent infections.
– Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water supports urinary tract health.
– Regular Medical Check-Ups: Routine exams can help detect and address potential issues early.
Conclusion
Pus cells in urine often indicate an underlying issue, such as an infection or inflammation in the urinary tract. By understanding the potential causes and symptoms, you can seek appropriate treatment and manage your health effectively. If you notice unusual changes in your urine or experience symptoms like pain, consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and personalized care.
For more insights on urinary health and other related topics, stay tuned to Myhealthadvise
Feel free to reach out with any questions or for further information on maintaining urinary health.